조합 알고리즘
1. 순열 표현 : nPr 서로 다른 n개 중의 r개를 뽑을때, 순서를 포함한 경우의 수 만약, 중복 가능한 n개 중 r개를 뽑으면, 중복 순열 2. 조합 표현 : nCr 서로 다른 n개 중의 r개를 뽑을때, 순서의 상관없
coding-food-court.tistory.com
1. 순열
표현 : nPr
서로 다른 n개 중의 r개를 뽑을때, 순서를 포함한 경우의 수
만약, 중복 가능한 n개 중 r개를 뽑으면, 중복 순열
2. 조합
표현 : nCr
서로 다른 n개 중의 r개를 뽑을때, 순서의 상관없이 뽑는 경우의 수
만약, 중복 가능한 n개 중 r개를 뽑으면, 중복 조합
3. 순열의 갯수
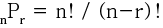
순열의 갯수는 위와 같은 공식으로 구할 수 있습니다. 그럼 factorial(팩토리얼) 재귀 함수를 구현하여 순열을 구현 할 수 있습니다.
public class Permutation2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.printf("nPr 사이즈 : %d", getPermutationSize(4, 4));
}
public static int getPermutationSize(int n, int r) {
if ((factorial(n - r)) <= 0)
return -1;
else
return factorial(n) / (factorial(n - r));
}
private static int factorial(int k) {
if (k <= 0)
return 1;
else
return k * factorial(k - 1);
}
}출력 결과
4. 순열 구하기
그럼, 순열의 경우들을 구하려면 어떻게 구현해야 할까요?
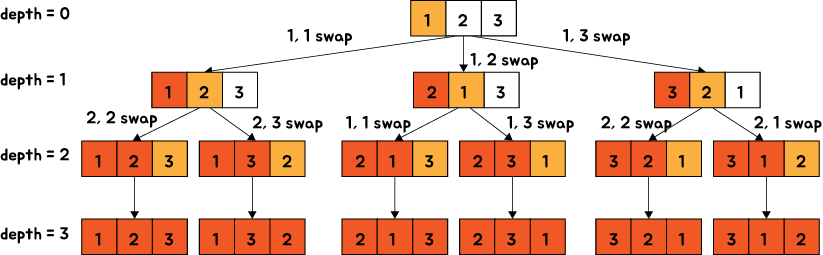
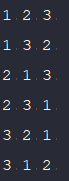
위 그림과 같이 접근 할 수 있습니다.
1. depth = 0에서 첫 인덱스의 값을 선택하고, 모든 인덱스를 돌면서, (1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3)을 swap 해줍니다.
2. depth = 1에서 두번째 인덱스를 선택하고, 두번째 인덱스와 마지막 인덱스의 값을 swap 해줍니다.
3. depth = 2에서 마지막 인덱스와 마지막 인덱스를 swap 해줍니다.
4. depth = 3에서 depth == r(뽑을려는 갯수) 같으므로, 해당 값을 출력해 줍니다.
java 소스 코드로 표현하면, 다음과 같습니다.
/*
* int[n] 중에서 r개의 순열 구하기
* 순열값을 출력 합니다.
* */
public class Permutation2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
doPermutation(arr, 0, 3, 3);
}
public static void doPermutation(int[] arr, int depth, int n, int r) {
// depth 가 r의 도달 하였으면, 한 사이클이 다돌았으므로 출력
if (depth == r) {
print(arr, r);
return;
}
for (int i = depth; i < n; i++) {
swap(arr, i, depth);
doPermutation(arr, depth + 1, n, r);
swap(arr, i, depth);
}
}
private static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int depth) {
int tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[depth];
arr[depth] = tmp;
}
public static void print(int[] arr, int r) {
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
System.out.printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}출력 결과
5. 순열값 반환
이번에는 바로 출력하는 시그니처 말고, ArrayList로 반환하는 시그니처로 구현 해보겠습니다.
import java.util.ArrayList;
/*
* int[n] 중에서 r개 의 순열 구하기
* ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> 로 순열값을 반환 한다.
* */
public class Permutation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
Permutation perm = new Permutation(3, 3);
perm.permutation(arr, 0);
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result = perm.getResult();
for (ArrayList<Integer> values : result) {
for (Integer value : values) {
System.out.printf("%d ", value);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
private int n;
private int r;
private ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result; // 모든 순열
// 전체 n개 갯수 중 r개를 뽑은 조합
public Permutation(int n, int r) {
this.n = n;
this.r = r;
this.result = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
}
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> getResult() {
return result;
}
public void permutation(int[] arr, int depth) {
// 현재 순열의 길이가 r일 때 결과 저장
if (depth == r) {
ArrayList<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
temp.add(arr[i]);
}
result.add(temp);
return;
}
for (int i = depth; i < n; i++) {
swap(arr, i, depth);
permutation(arr, depth + 1);
swap(arr, i, depth);
}
}
public void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}출력 결과
5. 시간 복잡도
위에서 이야기 했듯이, 순열 공식은 아래와 같습니다. 따라서, 위 순열 알고리즘의 시간 복잡도는 O(n!)이 되겠습니다.
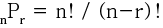
'Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 구간 합 구하기 알고리즘 (0) | 2020.10.07 |
|---|---|
| 투 포인터(Two Pointer) 알고리즘 (0) | 2020.10.07 |
| 조합 알고리즘 (0) | 2020.09.30 |
| 고정점 찾기 - 이것이 코딩 테스트다 with java (0) | 2020.09.24 |
| 경쟁적 전염 - 백준 18405 번 (0) | 2020.09.24 |