18428번: 감시 피하기
NxN 크기의 복도가 있다. 복도는 1x1 크기의 칸으로 나누어지며, 특정한 위치에는 선생님, 학생, 혹은 장애물이 위치할 수 있다. 현재 몇 명의 학생들은 수업시간에 몰래 복도로 빠져나왔는데, 복
www.acmicpc.net
1. 문제
n x n 의 복도가 주어졌습니다. 선생님과 학생의 위치가 n x n의 2차원 배열의 주어졌을때, 선생님은 상, 하, 좌, 우 로 학생이 있는지 감시 할수 있습니다. 그런데 선생님의 눈이 너무 좋아서 끝까지 학생이 있는지 없는지 확인 할 수 있습니다. 이때, 3개의 장애물을 설치 할 수 있습니다. 학생 앞의 장애물이 놓이면, 선생님은 학생을 발견 할 수 없습니다. 이때 선생님과 학생의 위치를 알 수 있는 n x n 의 2차원 배열이 주어 졌을 때, 3개의 장애물을 설치하여 학생이 선생님의 감시로 부터 피할수 있으면 "YES", 없으면 "NO" 를 출력 하시오.
2. 접근
1. n의 최대 갯수는 6이므로, n x n = 36 입니다.
2.
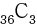
: 36개 중 3개의 장애물을 설치한다고 가정하면, 순서의 상관 없이 설치 하므로, = 7140 경우의 수가 가능 합니다. 7140 경우의 수는 제한 시간내의 충분히 탐색이 가능 합니다.
3. 따라서 선생님, 학생의 위치를 제외한 나머지 비어있는 위치 중 3가지 조합의 경우의 수를 DFS를 통해서 구합니다.
4. 조합 알고리즘의 경우, x, y 좌표를 모두 갖고 있는 Node 클래스를 정의하여 List<Node> 중 3개의 Node 조합을 찾아 냅니다.
5. 위에서 구한 경우의 수 중, 고정된 선생님의 위치를 기준으로 상,하,좌,우 형태로 탐색을 하며 학생이 발견되었는지, 발견 되지 않는지를 확인 합니다.
6. 조합 알고리즘을 DFS로 구현할때,

위와 같은 점화식을 세울수 있습니다.
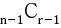
: 어떤 특정한 원소를 포함하고 뽑았을 경우
- 특정한 원소 1개를 이미 뽑았다고 가정하면, n-1개 중 r-1개를 뽑을 수 있습니다.
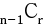
: 어떤 특정한 원소를 포함하지 않고 뽑았을 경우
- 특정한 원소 1개를 포함하지 않고 뽑는다면, n-1개 중 r개를 뽑아야 합니다.
밑에 java 소스에서 depth는 0부터 시작 하므로, depth + 1을 n - 1로 가정하고, Combination 클래스의 로직을 구현 하였습니다.
3. java 소스 코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class BOJ18428_2 {
// https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/18428
// 감시 피하기
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// N은 최대 6개 이므로 N x N = 36이다.
// 따라서 36 C 3 = 7140 이므로, 순차 탐색으로 모든 조합을 구할수 있다.
// 백트랙킹으로 모든 조합의 경우의 수를 모두 구하고,
// 해당 경우의 선생님의 시야의 학생이 들어오지 않으면, YES
// 학생이 들어오면 NO 출력
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
String[][] map = new String[n][n];
int r = 3;
BOJ18428_2 main = new BOJ18428_2();
ArrayList<Node> teachers = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Node> empties = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
String what = st.nextToken();
map[i][j] = what;
// 선생님들의 위치를 얻음
if (TEACHER.equals(what))
teachers.add(main.new Node(i, j));
// 비어있는 곳들의 위치를 얻음
if (EMPTY.equals(what))
empties.add(main.new Node(i, j));
}
}
br.close();
// 비어있는 곳들 중, 3개의 장애물을 설치할 조합들을 얻는다
Combination comb = main.new Combination(empties);
comb.doCombination(0, r);
ArrayList<ArrayList<Node>> whereToInstallObstacle = comb.getResult();
// 설치할 수 있으면 YES, 아니면, NO 출력
System.out.print(main.getCanInstallObstacleStatus(map, teachers, whereToInstallObstacle));
}
private String getCanInstallObstacleStatus(String[][] map, ArrayList<Node> teachers, ArrayList<ArrayList<Node>> installedMaps) {
return canInstall(installedMaps, teachers, map) ? YES : NO;
}
public boolean canInstall(ArrayList<ArrayList<Node>> installedMaps, ArrayList<Node> teachers, String[][] map) {
for (List<Node> installMap : installedMaps) {
// 장애물 설치
for (Node node : installMap) {
int x = node.getX();
int y = node.getY();
map[x][y] = OBSTACLE;
}
boolean canFindStudent = false;
// 모든 선생님이 학생 찾기
for (Node teacher : teachers) {
int tx = teacher.getX();
int ty = teacher.getY();
if (canFindStudentFromATeacher(tx, ty, map)) {
canFindStudent = true;
break;
}
}
// 모든 선생님이 학생을 찾을수 없다면, return true
if (!canFindStudent)
return true;
// 장애물 해제
for (Node node : installMap) {
int x = node.getX();
int y = node.getY();
map[x][y] = EMPTY;
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean canFindStudentFromATeacher(int tx, int ty, String[][] map) {
int n = map.length;
// 선생님을 기준으로 오른쪽 탐색
for (int i = ty + 1; i < n; i++) {
String whatRow = map[tx][i];
if (isStudent(whatRow)) {
return true;
} else if (isObstacle(whatRow)) {
break;
}else if (isTeacher(whatRow)) {
break;
}
}
// 선생님을 기준으로 왼쪽 탐색
for (int i = ty - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
String whatRow = map[tx][i];
if (isStudent(whatRow)) {
return true;
} else if (isObstacle(whatRow)) {
break;
}else if (isTeacher(whatRow)) {
break;
}
}
// 선생님을 기준으로 아래쪽 탐색
for (int i = tx + 1; i < n; i++) {
String whatRow = map[i][ty];
if (isStudent(whatRow)) {
return true;
} else if (isObstacle(whatRow)) {
break;
}else if (isTeacher(whatRow)) {
break;
}
}
// 선생님을 기준으로 위쪽 탐색
for (int i = tx - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
String whatRow = map[i][ty];
if (isStudent(whatRow)) {
return true;
} else if (isObstacle(whatRow)) {
break;
}else if (isTeacher(whatRow)) {
break;
}
}
return false;
}
public static final String EMPTY = "X";
public static final String OBSTACLE = "O";
public static final String TEACHER = "T";
public static final String STUDENT = "S";
public static final String YES = "YES";
public static final String NO = "NO";
private static boolean isStudent(String what) {
return STUDENT.equals(what);
}
private static boolean isTeacher(String what) {
return TEACHER.equals(what);
}
private static boolean isObstacle(String what) {
return OBSTACLE.equals(what);
}
class Combination {
private ArrayList<ArrayList<Node>> result; // 모든 조합
private ArrayList<Node> arr;
private int n;
private boolean[] visited;
public Combination(ArrayList<Node> arr) {
this.arr = arr;
this.n = arr.size();
this.visited = new boolean[arr.size()];
this.result = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Node>>();
}
// n 개중 r개를 뽑는 조합
public void doCombination(int depth, int r) {
if (r == 0) {
ArrayList<Node> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (visited[i]) {
tmp.add(arr.get(i));
}
}
result.add(tmp);
return;
}
if (depth == n) {
return;
}
// 특정 원소를 포함하고 뽑는 경우
visited[depth] = true;
doCombination(depth + 1, r - 1);
// 특정 원소를 포함하지 않고 뽑는 경우
visited[depth] = false;
doCombination(depth + 1, r);
}
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Node>> getResult() {
return result;
}
}
class Node {
private int x;
private int y;
public Node(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
}
}
3. 조합 알고리즘에 대해서
밑에 포스팅에서 조합 알고리즘을 더 자세하게 다루었습니다.
조합 알고리즘
1. 순열 표현 : nPr 서로 다른 n개 중의 r개를 뽑을때, 순서를 포함한 경우의 수 만약, 중복 가능한 n개 중 r개를 뽑으면, 중복 순열 2. 조합 표현 : nCr 서로 다른 n개 중의 r개를 뽑을때, 순서의 상관없
coding-food-court.tistory.com
'Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 14888번 - '연산자 끼워넣기' (0) | 2020.10.23 |
|---|---|
| 백준 18352번 - '특정 거리의 도시 찾기' (0) | 2020.10.16 |
| 구간 합 구하기 알고리즘 (0) | 2020.10.07 |
| 투 포인터(Two Pointer) 알고리즘 (0) | 2020.10.07 |
| 순열 알고리즘 (0) | 2020.10.02 |